There are a few common network error codes that can occur when troubleshooting network connectivity issues. These error codes are generally caused by a misconfiguration or an issue with the network itself.
The most common error code is "404 Not Found". This error code means that the requested resource could not be found on the server. This can be caused by a misconfiguration in the server's routing table, or by the requested resource simply not existing on the server.
Another common error code is "502 Bad Gateway". This error code means that the server was unable to connect to the upstream server. This can be caused by a firewall blocking the connection, or by the upstream server being down.
Finally, the "503 Service Unavailable" error code means that the server is currently unavailable. This can be caused by the server being down for maintenance, or by a heavy load causing the server to be unresponsive.
1. Restart the computer
To restart the computer, you may need to press the power button to turn it off and on again. After turning on the computer, wait a few seconds for it to finish loading the operating system. From the Start menu, select Control Panel. Select System and Security. Select Restart. Select Yes in the dialog box that appears. Select the appropriate option to restart your computer.
2. Check the network connections
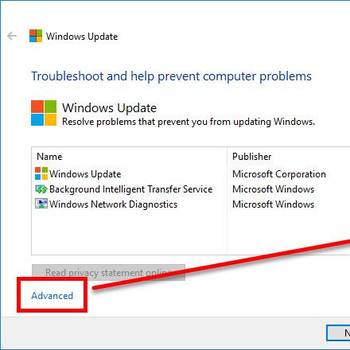
- In order to see if the network connection is working, open the Windows Networking Troubleshooter.
- Click on "Test network connection."
- If the connection is not working, the computer will give you an error code.
- To fix the error code, you will need to: a. Check the cables. b. Check for proper configuration of the network adapter. c. Check for viruses and malware.
3. Check the firewall settings
In order to check the firewall settings, open a command prompt and type "netsh advfirewall show currentstate". This will give you a list of firewall settings. To fix a common network error code, you will need to change the settings that are causing the issue.
4. Check the ISP settings
- In your web browser, type "cmd" and press Enter.
- Type "ipconfig /all" and press Enter.
- Look for the line that says "Default Gateway" and look for the IP address that is listed.
- If the IP address is not the same as the IP address that is listed in your router, then you will need to change the Default Gateway setting in your router.
- Next, type "cmd" and press Enter.
- Type "netsh int ip reset" and press Enter.
- Type "netsh int ip add address <IP Address> mask <Mask><Prefix> " and press Enter.
- Type "cmd" and press Enter.
- Type "netsh interface ipv4 show interface" and press Enter.
- Look for the line that says "IPv4 Address" and look for the address that is listed.
- If the address is not the same as the address that is listed in your router, then you will need to change the IPv4 Address setting in your router.
- Next, type "cmd" and press Enter.
- Type "netsh interface ipv6 show interface" and press Enter.
- Look for the line that says "IPv6 Address" and look for the address that is listed.
- If the address is not the same as the address that is listed in your router, then you will need to change the IPv6 Address setting in your router.
5. Check the DNS settings
- Open the "control panel"
- Click on "Network and Internet"
- Under "Network and Sharing Center" click on "DNS"
- On the "DNS" window, you will see a list of current DNS servers. You can either type in the IP address of a different DNS server, or click on the "Automatic" button to have Windows 10 try to find a DNS server for you.
- If your Network is not working correctly, you can also try to troubleshoot the DNS settings by clicking on "Resolve Issues" and then selecting "DNS" from the "Problem Type" list.
- In the "Resolve Issues" window, you will see a list of common Network error codes. If your Network is not working correctly, you can try to fix the DNS settings by selecting the corresponding error code and then clicking on the "Resolve" button.
Some users might also have success with the following opitons:
- Check the router settings.
- Update the network drivers.
- Reset the TCP/IP stack.
- Disable the antivirus software.
- Use the Windows Network Diagnostics tool.