Windows Xp error codes are often caused by corrupt or missing files. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including viruses, hardware failures, and software conflicts. When these files become corrupt or are missing, Windows is unable to load them, and the system will generate an error code. These codes can be difficult to troubleshoot, as they may not provide any specific information about the cause of the problem. In some cases, however, they can help you pinpoint the root cause of the issue and find a solution.
![Depressed teenager using laptop on floor in room]() Windows 10irql_not_less_or_equal error (Windows 10, 8, 7, XP & Vista)
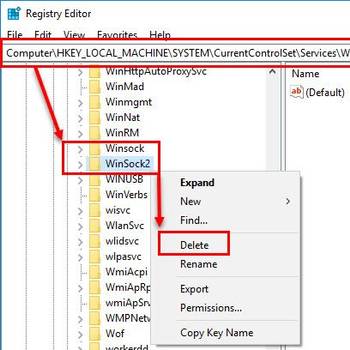
Windows 10irql_not_less_or_equal error (Windows 10, 8, 7, XP & Vista)![Delete Winsock keys and reinstall TCP/IP]() Windows 7Windows Sockets Registry Entries Missing (Win 10, 7, XP & Vista)Windows Sockets Registry Entries Missing is an error that may indicate a corruption inside Windows Sockets (Winsock) registry entries. Winsock is a programming interface, which acts as a supporting program by managing the incoming and outgoing network requests. If Winsock is unable to process the requests, users will not be able to connect to the internet.
Windows 7Windows Sockets Registry Entries Missing (Win 10, 7, XP & Vista)Windows Sockets Registry Entries Missing is an error that may indicate a corruption inside Windows Sockets (Winsock) registry entries. Winsock is a programming interface, which acts as a supporting program by managing the incoming and outgoing network requests. If Winsock is unable to process the requests, users will not be able to connect to the internet.
1. Restart your computer
1.Click on the Start button 2.Select Control Panel 3.Select System and Security 4.Select Restart 5.Select the appropriate option for your computer 6.Enter your computer's BIOS or UEFI password if prompted
2. Check for updates
- Open the Control Panel.
- Click on System and Security.
- Click on Windows Update.
- If there are any updates available, they will be listed.
- To install the updates, click on the “Update” button.
- If there are any problems with the updates, they will be listed.
- To restore the computer to its previous state, click on the “Restore” button.
3. Run a virus scan
- Open the Start Menu and select Settings.
- Select Control Panel.
- Select System and Security.
- Select Virus Protection.
- Select Run a virus scan.
- Select the type of scan you want to run.
- Select a scan target.
- Select a scan type.
- Select a scan schedule.
- Select a scan resolution.
- Select a scan location.
- Review the scan results.
4. Run a registry cleaner
1.Open Windows Explorer and navigate to the following path: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters 2.Once you are in the Parameters folder, right-click on the "Interfaces" key and select "New" from the context menu. 3.Enter the following values in the "Name" field: "Local Area Connection" and "Description" and click on the "OK" button. 4.Right-click on the "Local Area Connection" key and select "New" from the context menu. 5.Enter the following values in the "Name" field: "Default Gateway" and "Description" and click on the "OK" button. 6.Right-click on the "Default Gateway" key and select "New" from the context menu. 7.Enter the following values in the "Name" field: "DNS Servers" and "Description" and click on the "OK" button. 8.Select the "Enable TCP/IP Forwarding" checkbox and click on the "OK" button. 9.Click on the "File" tab and select "New" from the context menu. 10.Enter the following values in the "Name" field: "Tcpip.exe" and click on the "OK" button. 11.Click on the "Start" button and then on the "Run" button. 12.Type the following command into the "Run" dialog box and press the "Enter" button: tcpip.exe 13.Click on the "OK" button to exit the TCP/IP registry cleaner.
If you didn't find success with an option above, then try:
- Reinstall Windows. This should be a last resort, as it will delete all of your data.